Savings
As mentioned above, Personal Finance revolves around 3 main issues:
1 — Make money
2 — Accumulate money (savings and spend management)
3 — Protect money
In Chapter 1, you took a closer look at sources of income and how to diversify our sources of income.
In this chapter, you’ll look at another important element besides income generation: Savings – a way to handle income to both accumulate assets and ensure reasonable spending needs in life.
First, you need to understand that: Accumulation is a process of saving funds that are left over after deducting necessary expenses from income over a given a period of time. It is not easy to save as much money as possible without feeling pressure. Meanwhile, your investment needs (education, social relations) also need to be met.
In general, accumulation includes 2 main actions, namely savings and spend management. Savings include:
Accounts to repay debts on time (required)
Provisions for 3 - 6 months of living expenses for essential needs and potential uncertainties.
Long-term savings
Depending on your abilities and needs, you should calculate the percentage of the above items for each stage in life. And this will be deducted first when you receive income.
Recommended level (monthly)
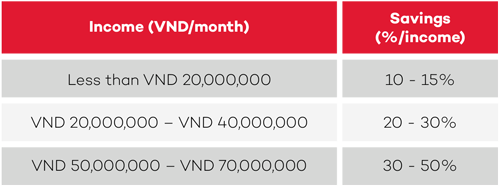
If you have no dependents, your savings can increase by 5 - 10% and vice versa (if you provide financial support for 2 people, your savings will be further reduced by 5 - 10% ).
For example, Mai’s current income is VND 7,000,000/month. Based on this income, her standard monthly savings will range from VND 700,000 to VND 1,050,000. However, since Mai doesn't have to support anyone, she can increase her savings by 5 - 10% . Thus, Mai can increase her monthly savings by up to VND 1,400,000. Tuan’s standard savings amount, meanwhile, ranges from VND 5,000,000 to VND 7,500,000. However, since Tuan needs to deduct a fixed monthly income to support his parents in the countryside and his younger brother to go to college, his monthly savings can be reduced to between VND 3,750,000 and VND 6,250,000. If he needs to support his family more, this amount can be reduced to VND 2,500,000 – VND 3,750,000 per month.
What should you do with the savings?
(sorted by priority)
1. DEBT REPAYMENT
This is the most important priority. Debt not only puts financial pressure on your personal life, but the interest rate of a bank loan is always much higher than the interest rate of a savings deposit. Therefore, paying off debt should be your top priority after you’ve taken care of your required expenses for the period. Note: Before deciding on a loan, it is necessary to determine the loan interest and periodic debt. The principle here is to ensure that the income after deducting essential expenses must be able to pay the monthly interest and principal debt.
2. PROVISIONS
This amount is used to cover unexpected and unusual needs such as illness, unemployment, and support for loved ones. It helps to maintain important living expenses for a given period before you consider high-interest loans or liquidating assets to find money for your living expenses. If you haven’t accumulated enough money for your basic living expenses for the next 3 to 6 months, you should consider saving 2 - 3% of your monthly income for provisions.
3. SAVINGS
This is the capital to create passive income. As mentioned in Chapter 1, a simple and effective way to save is to open a term deposit account (preferably at a small-sized bank to get a better interest rate). In addition, if you have accumulated a decent amount of savings, you can buy some assets in line with your knowledge, information, and risk tolerance (you’ll learn more about investment in Chapter 5).